Eye Tumors
Eyelid Tumors
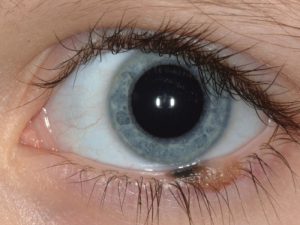
Nevus
Benign pigmented or nonpigmented lesion on the eyelid or eyelid margin with rare tendency for malignant transformation.
Papilloma
Benign, slowly evolving tumor of the eyelid mostly found in the elderly.
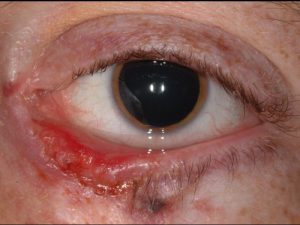
Chalazion
Benign, inflammatory tumor of the sebaceous gland.
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Malignant tumor arising from the epidermis that can appear as a nodular, nodulo-ulcerative, or sclerosing lesion. Complete resection is important.
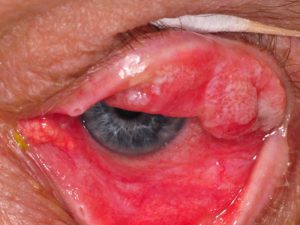
Sebaceous Carcinoma
Malignant tumor arising from the sebaceous glands that can invade the surface of the eye and grow into the orbit. This tumor tends to arise in elderly women most often and has a greasy yellow color and loss of eyelashes. Complete resection is important.
Squamous Cell CarcinomaMalignant tumor of the epidermis in patients with heavy sun exposure. This can be treated surgically or with topical creams.
Conjunctiva Tumors
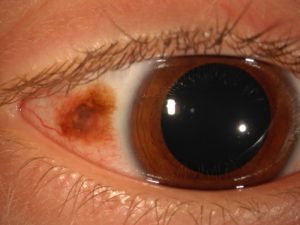
Pingueculum
Benign degenerative tissue on the eye in the sun exposed regions that can look like an ocular surface tumor.
Pterygium
Benign tumor on the eye in which the conjunctival tissue overgrows onto the cornea. This can simulated squamous cell carcinoma.
Cyst
Benign fluid-filled lesion.
Nevus
Benign pigmented or nonpigmented mass on the eye surface. This is the most common tumor of the conjunctiva. Detection occurs in children and young adults.
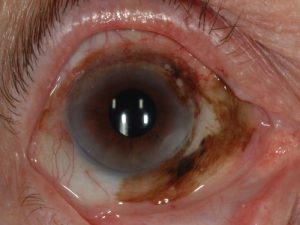
Primary acquired melanosis
Prelmalignant pigmented condition causing brown discoloration of the ocular surface. This condition carries relatively high rate for transformation into melanoma.
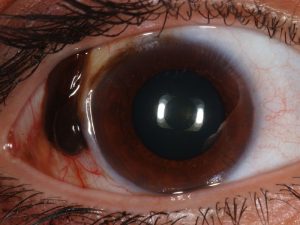
MelanomaMalignant tumor of the conjunctiva that arises from long-standing nevus, primary acquired melanosis, or de novo. Early, complete resection is important.
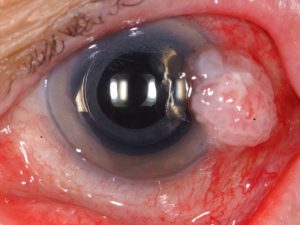
Squamous Cell CarcinomaMalignant tumor appearing as a foamy, yellow-white vascular mass on the ocular surface. Treatment can be surgical or with eyedrops.
Lymphoma
Malignant tumor that can occur with systemic lymphoma. Tends to hide in the upper or lower quadrants deep behind the eyelids.
INTRAOCULAR TUMORS
Iris
Cyst
Benign condition that can occur in the iris stroma (front of iris) or iris pigment epithelium (back of iris). Some can be observed while others need surgical treatment.
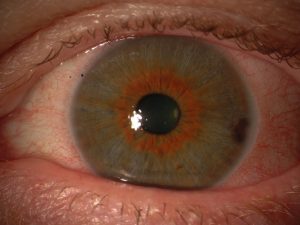
Nevus
Benign tumor appearing as a brown or yellows spot on the iris stroma.
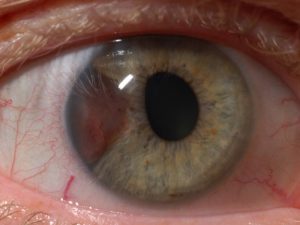
Melanoma
Malignant tumor often detected when small size so prognosis is usually favorable.
Choroid
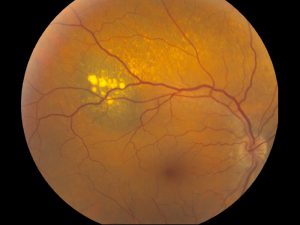
Nevus
Benign tumor that classically remains stable. Can lead to reduced visual acuity. Can transform into melanoma.
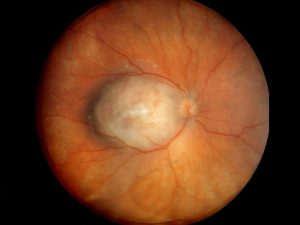
Melanoma
Malignant tumor with relatively high risk for metastasis. Classified into small, medium, or large sizes. Often treated with radiation or eye removal.
Hemangioma
Benign tumor that can leak and result in poor vision.
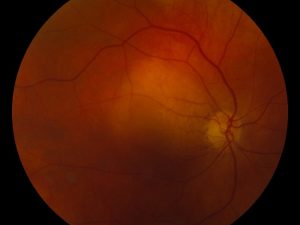
Metastasis
Malignant tumor that spread to the inner eye from remote site such as cancer of the breast or lung.
Lymphoma
Malignant tumor often associated with similar tumor in the abdomen.
Pseudomelanoma
Conditions that simulate malignant melanoma.
Nevus
Benign tumor.
Peripheral exudative hemorrhagic chorioretinopathy
Hemorrhagic retinal disease of the elderly.
Retina
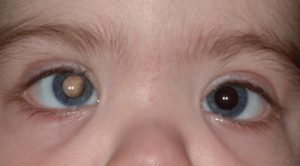
Retinoblastoma
Clinical features- Most common presentation is with leukocoria (white pupil) or strabismus (crossed eye). The tumor appears as a yellow-white mass in the retina of small , medium, or large size. Often there is a large retinal detachment.
Genetic testing – Performed on all children to investigate chromosome 13.
Treatment
Intravenous chemotherapy (chemoreduction)
Subtenon’s chemotherapy
Intra-arterial chemotherapy (IAC)
Intravitreal chemotherapy (melphalan)
Plaque radiotherapy
Cryotherapy/Thermotherapy
Enucleation
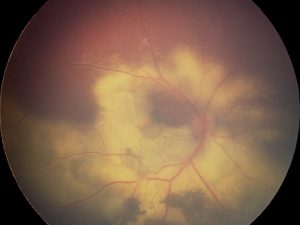
Astrocytic hamartoma
Benign retinal tumor, sometimes found with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex.
Coats disease
Benign vascular abnormality where the retinal vessels leak yellow exudation and fluid.
Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy
Benign vascular condition with leakage and possible hereditary trait.
Vasoproliferative tumor
Benign vascular tumor with leakage.
Hemangioblastoma
Benign vascular tumor with leakage, and often associated with von Hippel Lindau disease.
Lymphoma
Malignant tumor of the retina and vitreous that can be associated with brain lymphoma.
Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)
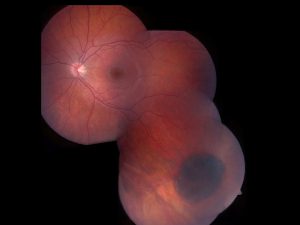
Combined hamartoma
Congenital benign tumor that often leads to poor vision.
Congenital hypertrophy of the RPE
Benign flat tumor often confused with nevus or melanoma.
Adenoma/Adenocarcinoma
Rare tumor that is nodular, pigmented and slowly grows over many years.
Sclera
Sclerochoroidal calcification
Benign chronic calcification of the eye wall.
Solitary idiopathic choroiditis
Benign inflammatory focus of the eye wall.
ORBIT TUMORS
Inflammatory
Pseudotumor (idiopathic orbital inflammation)Rapid onset inflammation and pain in the tissues around the eye. Responds to oral prednisone.
Vascular
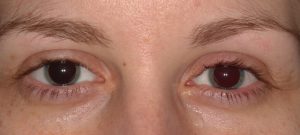
Capillary hemangiomaBenign red skin tumor that has onset after birth and grows until about 6 months of age then undergoes slow spontaneous involution. LymphangiomaBenign, often ill-defined, tumor of the lymphatics. Cavernous hemangiomaBenign tumor with large cavernous spaces filled with blood.
Lymphoid
Benign reactive lymphoid hyperplasiaBenign tumor comprised of lymphocytes. Can achieve a large size before discovery. LymphomaMucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) – Malignant low-grade tumor that can be associated with lymphoma in the abdomen. Can respond to surgical removal or systemic medications. MetastasisMalignant tumors that spread to the orbit through the blood stream from remote sites like cancer of the breast, lung, or prostate.
Lacrimal Gland
PseudotumorInflammation of the lacrimal gland. LymphomaMalignant tumor with lymphocytes. Pleomorphic adenomaBenign tumor that arises from the lacrimal gland structures and remains localized to the orbit. Adenoid cystic carcinomaMalignant tumor arising from the lacrimal gland with propensity to grow into surrounding tissue and spread to other organs.
PATHOLOGY
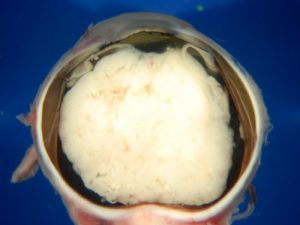
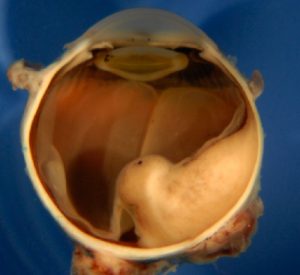
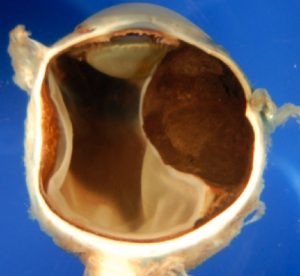
RetinoblastomaGlobe filled with retinoblastoma appearing as a white mass. MelanomaGlobe filled with pigmented (brown) or nonpigmented (yellow) mass.
